- December 25, 2015
- Posted by: isoqaruser
- Categories:


WHAT IS ISO 22301:2012?
ISO 22301 is the Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) standard that has been developed to protect companies from the risks associated with downtime which can occur due to unexpected disruptions or disasters. Disruptions to your business can result in revenue loss, data risk breakdowns and failure to deliver normal client services as per service level agreements. ISO 22301specifies the requirements for a management system to protect against, reduce the likelihood of, and ensure your business recovers from disruptive incidents.
BENEFITS OF ISO 22301 BUSINESS CONTINUITY MANAGEMENT-
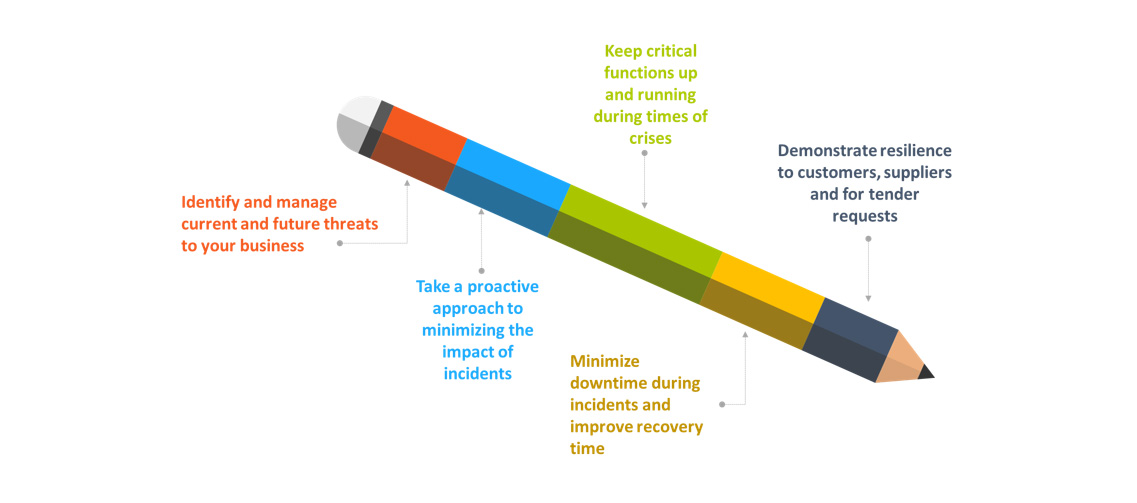
WHY IMPLEMENT A BUSINESS CONTINUITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (BCMS)?
The ISO 22301 standard defines a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) as:
Part of the over-management system that establishes, implements, operates, monitors, reviews, maintains and improves business continuity.
To mitigate the effects of disruption, it is essential that all organizations prepare and manage business continuity plans. A BCMS enables organizations to update, control and deploy these plans and align them with their strategic and operational objectives.
Many organizations believe that if they have a business continuity plan (BCP) in place, they will be able to respond to an incident in an appropriate way. Whilst a BCP will provide members of the response team with guidance as to what they are supposed to do if an incident occurs, it is usually not part of a formal management system.
A BCMS, on the other hand, is broadly accepted as the most comprehensive approach to organizational resilience. It enables organizations to update, control and deploy effective plans, taking into account organizational contingencies and capabilities as well as the business needs
APPROACH TO BCMS IMPLEMENTATION:
- Define BCMS Scope in line with the context determined and needs and expectation of interested parties.
- Define BCMS policy and identify BCMS related organizational objectives.
- Identify continuity related contractual and legal requirements.
- Identify all business processes supporting your services.
- Carry out BIA (Business Impact Assessment) for these processes – Impact vs time curve. Based on the acceptable level of impact determined by the organization and the maximum impact criteria determine the RTO and MAO of these processes.
- Determine the RPO based on business and contractual/regulatory needs.
- Carry out the risk assessment based on the risk methodology adopted.
- Determine resilience control requirements- Pro Active system.
- Design the BCP based on the risk scenario identified and the determined RTO/RPO/MAO requirements. Establish the warning & communication system/call tree system etc.
- Establish BCP exercising methods and processes.
- Test BCP.
- Establish good monitoring and measurement system and associated management support processes.
- Detail the roles and responsibilities related to business continuity and the associated competency requirements.
COMMAND LEVELS WHILE IMPLEMENTING BCMS
- It is common for organisations to split the organisation into levels (so-called Command levels) when it comes to BCP.
- The Gold-Silver-Bronze level is common because of its use by UK emergency services and the police. Gold level is often described as those who can sign the cheques; in a BCP it is wise to remember access to financial resources can be critical.
- This helps focus decision making and activities and determine actions to be taken where and when.

WHAT INDUSTRIES SHOULD IMPLEMENT ISO 22301:2012
ISO 22301 is best suited to organizations that do not have the luxury of managing downtime without disruption. Any industry where dis continuity can have a major impact on the end users/ customers’ needs to apply BCMS. As markets grow more competitive implementing systems like ISO 22301 can mean the difference in retaining and growing your client base. ISO 22301 certification is the perfect option for an organization who needs to ensure clients, staff, and stakeholders that have a plan in place to manage disruptions that minimize downtime.
PROFESSIONAL ADVICE:
- The BCI (Business Continuity Institute) is a professional organisation dedicated to the industry with its own web site and Quarterly magazine (available online). http://thebci.org
- Other sources might be specific industry bodies.
The BCI has a guide on International Legislation and regulations, standards and good practice. At the moment there are very few truly International requirements and most relate to Banking and Finance;
- High-Level Principles for Business Continuity – Basel Joint Forum.
- Basel II – Capital Accord
- Basel III
The second 2 are issued by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision and mostly relate to Management Structure, Risk and communications.
CONCLUSION:
It’s very correctly said “SURVIVAL OF THE FITTEST”. To survive organization needs both proactive and reactive strategy and systems. In today’s scenario, disruption is unacceptable to any customer/ end user. We all need seamless services. Minimize the business impact by adopting a robust business continuity management system.
Risk management – Before an incident and BCMS – after an incident. These are two components business needs today to survive in the competitive world.
